

This app creates a live-usb from an iso-file, another live-usb, a live-cd/dvd or a running live system. The main screen contains four areas

This top section is often all that a user needs to consider. With the two buttons on the left you select the USB you want to use (the box will be pre-populated with usbs that are connected when the MX-LUM starts), navigate to the ISO you want, and click the Next buttton at the bottom of the screen. The top right button (refresh) can be used if your USB device is plugged after MX-LUM starts, while the bottom right button toggles Advanced options (below).
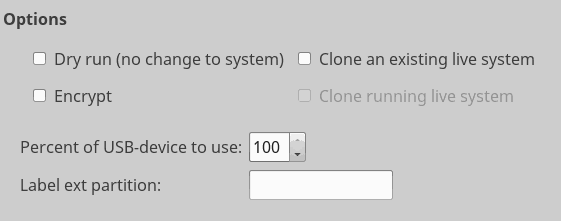
Dry Run simulates what will happen with the configuration chosen. Nothing is actually written to disk.
Encrypt allows the user to create a fully encyrpted live-USB using LUKS encryption.
Clone an existing live system will allow the user to clone a previously created live-USB.
Clone running live system allows live system users to clone the live system that is currently running onto a usb.
Percent of USB-device to use allows you to set a limit on how much of the device is used for the live system.
Lable ext partition allows you to utilize a custom label for the fileystem on the live-USB

Full-featured mode is available for users of antiX/MX family systems, including snapshots. This mode enables all the live system features, including peristence and other features requiring writable media to function (save options, etc…).
Image mode is the fallback for non-antiX/MX family isos, and utilizes a “dd” backend to create an exact copy of a source iso onto the target media. This is similar to utilities like etcher or using “dd” directly from the commandline. Image Mode has some sanity checks to help the user write data only to the target media.
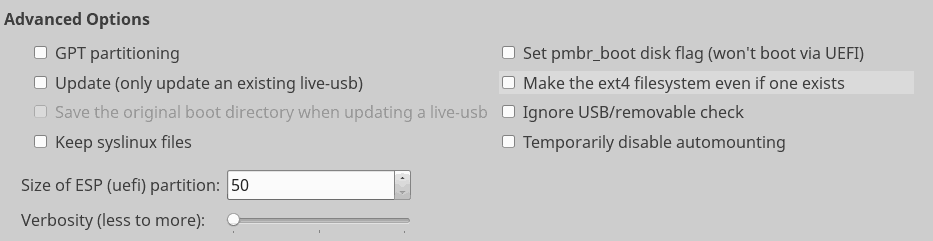
The advanced options are mostly for testing and develoment work, although some might be useful to end users in particular scenarios.
GPT Paritioning forces the use of gpt partition tables on the live-usb insted of the default “msdos” partition table. Some systems may not boot from the live-USB if gpt is used, and this is only really usefull in UEFI environements.
Update allows the user to update an existing live-USB with a new iso. this is not useful if persistence is in use, and is usually only used for testing and development work.
Save the original boot directory when updating a live-USB is useful when an encrypted environment is in use and is generally only used for testing and development.
Temporarily disable automounting is useful to disable antiX automounting system, and has no effect in MX.
Ignore USB/removable check skips the final sanity checks to make sure a target media is a removable device.
Set pmbr_boot disk flag sets the legacy boot flag on gpt partitions, but disables booting from UEFI systems.
Keep syslinux files will disable reinstallation of syslinux boot loader on an exisitng live-USB, and typically only matters for development work.
Make ext filesystem even if one exists forces creation of a new ext filesystem even if one exists already. Generally only useful for testing and development.
Resources
BitJam’s detailed notes can be found here.
Development history: BitJam (antiX), Dolphin_Oracle, adrian
License: ?
v. 20181104